“Deep Generative Factorization For Speech Signal(ICASSP21)”版本间的差异
来自cslt Wiki
| 第44行: | 第44行: | ||
NF | 0.013 | 0.410 | 0.397 || 0.612 | 0.489 | -0.123 | NF | 0.013 | 0.410 | 0.397 || 0.612 | 0.489 | -0.123 | ||
DNF | 0.013 | 0.619 | 0.606 || 0.612 | 0.335 | -0.277 | DNF | 0.013 | 0.619 | 0.606 || 0.612 | 0.335 | -0.277 | ||
| − | f-DNF | 0.013 | <b>0.636</b> | + | f-DNF | 0.013 | <b>0.636</b> | <b>0.623</b> || 0.612 | <b>0.536</b> | <b>-0.076</b> |
----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| 第50行: | 第50行: | ||
<b>Speaker Manipulation</b> | <b>Speaker Manipulation</b> | ||
Model | <i>p(s<sub>2</sub>|x)</i> | <i>p(s<sub>2</sub>|x')</i> | <i>δ(s<sub>2</sub>)</i> || <i>p(q|x)</i> | <i>p(q|x')</i> | <i>δ(q)</i> | Model | <i>p(s<sub>2</sub>|x)</i> | <i>p(s<sub>2</sub>|x')</i> | <i>δ(s<sub>2</sub>)</i> || <i>p(q|x)</i> | <i>p(q|x')</i> | <i>δ(q)</i> | ||
| − | VAE | 0.010 | 0.303 | 0.293 || 0.520 | <b>0.509</b> | + | VAE | 0.010 | 0.303 | 0.293 || 0.520 | <b>0.509</b> | <b>-0.011</b> |
NF | 0.010 | 0.435 | 0.425 || 0.520 | 0.484 | -0.036 | NF | 0.010 | 0.435 | 0.425 || 0.520 | 0.484 | -0.036 | ||
DNF | 0.010 | 0.700 | 0.690 || 0.520 | 0.349 | -0.171 | DNF | 0.010 | 0.700 | 0.690 || 0.520 | 0.349 | -0.171 | ||
| − | f-DNF | 0.010 | <b>0.710</b> | + | f-DNF | 0.010 | <b>0.710</b> | <b>0.700</b> || 0.520 | 0.503 | -0.017 |
----------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ||
2020年10月23日 (五) 07:49的版本
目录
Introduction
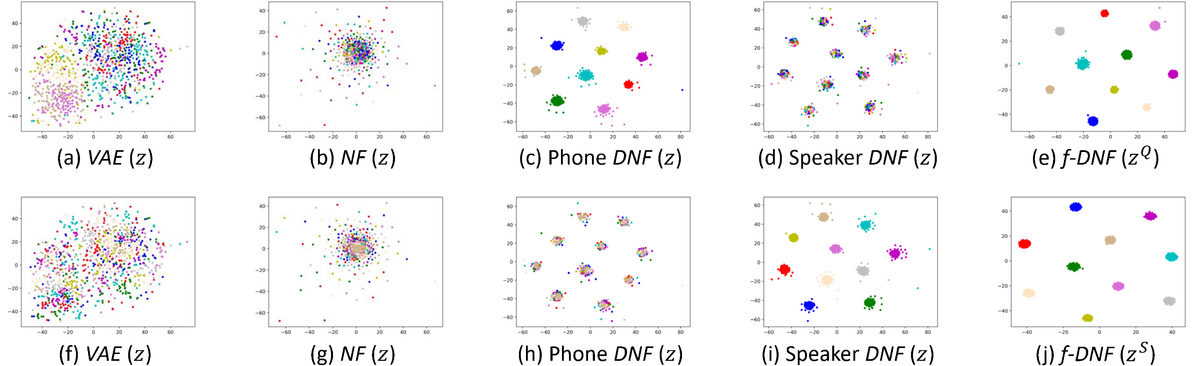
- This paper presented a speech information factorization method based on a novel deep generative model that we called factorial discriminative normalization flow.
Qualitative and quantitative experimental results show that compared to all other models, the proposed factorial DNF can retain the class structure corresponding to multiple information factors, and changing one factor will cause little distortion on other factors. This demonstrates that factorial DNF can well factorize speech signal into different information factors.
Members
- Haoran Sun, Lantian Li, Yunqi Cai, Yang Zhang, Thomas Fang Zheng, Dong Wang
Publications
- Haoran Sun, Lantian Li, Yunqi Cai, Yang Zhang, Thomas Fang Zheng, Dong Wang, "Deep Generative Factorization For Speech Signal", 2020. pdf
Source Code
- xxx
Factorial DNF
- xxx
Experiments
Data
- xx
Encoding
- xx
Factor manipulation
Phone Manipulation Model | p(q2|x) | p(q2|x') | δ(q2) || p(s|x) | p(s|x') | δ(s) VAE | 0.013 | 0.312 | 0.299 || 0.612 | 0.454 | -0.158 NF | 0.013 | 0.410 | 0.397 || 0.612 | 0.489 | -0.123 DNF | 0.013 | 0.619 | 0.606 || 0.612 | 0.335 | -0.277 f-DNF | 0.013 | 0.636 | 0.623 || 0.612 | 0.536 | -0.076
Speaker Manipulation Model | p(s2|x) | p(s2|x') | δ(s2) || p(q|x) | p(q|x') | δ(q) VAE | 0.010 | 0.303 | 0.293 || 0.520 | 0.509 | -0.011 NF | 0.010 | 0.435 | 0.425 || 0.520 | 0.484 | -0.036 DNF | 0.010 | 0.700 | 0.690 || 0.520 | 0.349 | -0.171 f-DNF | 0.010 | 0.710 | 0.700 || 0.520 | 0.503 | -0.017
Future Work
- Test factorial DNF on larger datasets.
- Establish general theories for deep generative factorization.