“Flow-based Speech Analysis”版本间的差异
来自cslt Wiki
(→Flow-based Speech Analysis) |
(→Publications) |
||
| (2位用户的53个中间修订版本未显示) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Introduction=== | ===Introduction=== | ||
| − | * We present a preliminary investigation on unsupervised speech factorization based on the normalization flow model. This model constructs a complex invertible transform, by which we can project speech segments into a latent code space where the distribution is a simple diagonal Gaussian. | + | |
| − | * Our preliminary investigation on the TIMIT database shows that this code space exhibits favorable properties such as denseness and pseudo linearity, and perceptually important factors such as phonetic content and speaker trait can be represented as particular directions within the code space. | + | * We present a preliminary investigation on unsupervised speech factorization based on the normalization flow model. |
| + | This model constructs a complex invertible transform, by which we can project speech segments into a latent code space where the distribution is a simple diagonal Gaussian. | ||
| + | * Our preliminary investigation on the TIMIT database shows that this code space exhibits favorable properties such as denseness and pseudo linearity, | ||
| + | and perceptually important factors such as phonetic content and speaker trait can be represented as particular directions within the code space. | ||
* <b>Index Terms:</b> speech factorization, normalization flow, deep learning | * <b>Index Terms:</b> speech factorization, normalization flow, deep learning | ||
| − | === | + | ===Members=== |
| − | * | + | |
| − | [[文件:Fig3_flow.jpg| | + | * Dong Wang, Haoran Sun, Yunqi Cai, Lantian Li |
| + | |||
| + | ===Publications=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Haoran Sun, Yunqi Cai, Lantian Li, Dong Wang, "On Investigation of Unsupervised Speech Factorization Based in Normalization Flow", 2019. [[媒体文件:Flow.pdf|pdf]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Source Code=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Glow model implemented by Yuki-Chai in PyTorch. [https://github.com/chaiyujin/glow-pytorch glow-pytorch] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Experiments=== | ||
| + | |||
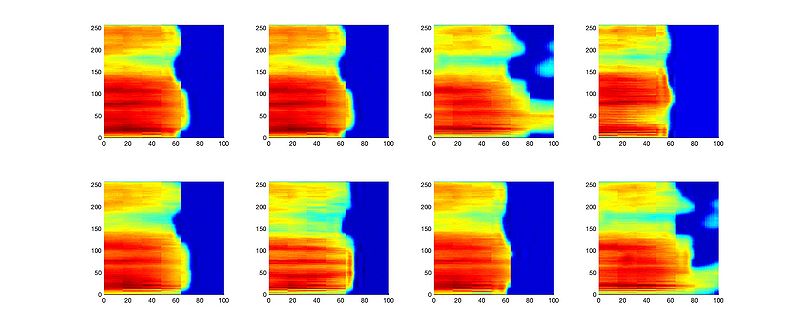
| + | *<b> Right click "figs" or "wavs" and select "save as" to save the spectrogram figures or related audio files. </b> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Sampling: [[媒体文件:Figs3_flow.rar|figs]] [[媒体文件:Wav_fig3.rar|wavs]] (right click) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[文件:Fig3_flow.jpg|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
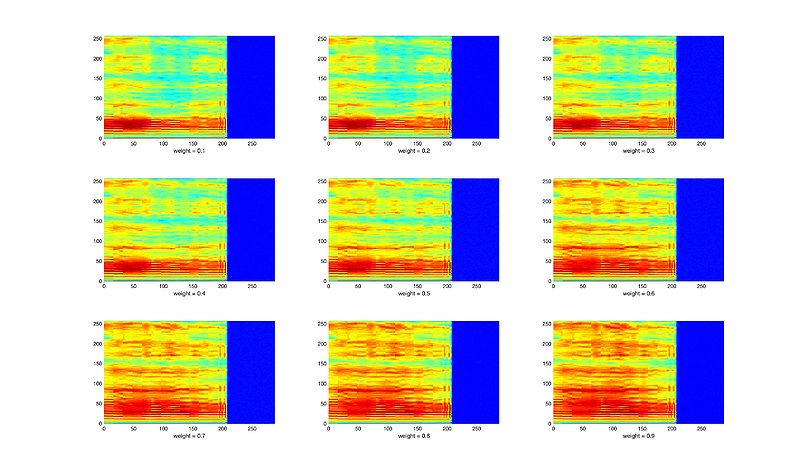
| + | * Interpolation: [[媒体文件:Figs4_flow.rar|figs]] [[媒体文件:Wav_fig4.rar|wavs]] (right click) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[文件:Fig4_flow.jpg|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
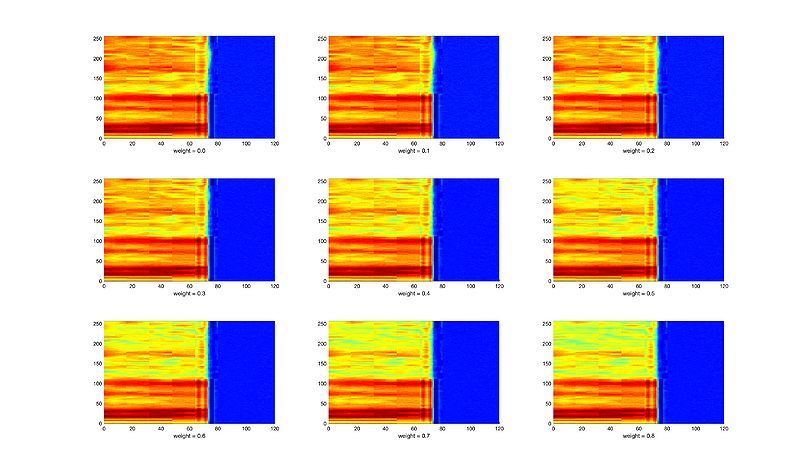
| + | * Denoising: [[媒体文件:Figs5_flow.rar|figs]] [[媒体文件:Wav_fig5.rar|wavs]] (right click) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[文件:Fig5_flow.jpg|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Future Work=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * To conduct more thorough studies on large databases and continuous speech. | ||
| + | * To investigate discriminative flow models which take class information into consideration. | ||
2019年10月29日 (二) 12:58的最后版本
Introduction
- We present a preliminary investigation on unsupervised speech factorization based on the normalization flow model.
This model constructs a complex invertible transform, by which we can project speech segments into a latent code space where the distribution is a simple diagonal Gaussian.
- Our preliminary investigation on the TIMIT database shows that this code space exhibits favorable properties such as denseness and pseudo linearity,
and perceptually important factors such as phonetic content and speaker trait can be represented as particular directions within the code space.
- Index Terms: speech factorization, normalization flow, deep learning
Members
- Dong Wang, Haoran Sun, Yunqi Cai, Lantian Li
Publications
- Haoran Sun, Yunqi Cai, Lantian Li, Dong Wang, "On Investigation of Unsupervised Speech Factorization Based in Normalization Flow", 2019. pdf
Source Code
- Glow model implemented by Yuki-Chai in PyTorch. glow-pytorch
Experiments
- Right click "figs" or "wavs" and select "save as" to save the spectrogram figures or related audio files.
Future Work
- To conduct more thorough studies on large databases and continuous speech.
- To investigate discriminative flow models which take class information into consideration.